Vertical or Horizontal, Deep or Shallow: Evolving the Marketplace Model
Published by maria gbaf
Posted on October 20, 2021
7 min readLast updated: January 29, 2026

Published by maria gbaf
Posted on October 20, 2021
7 min readLast updated: January 29, 2026

Marketplaces in finance are evolving with vertical and horizontal models, offering deep and shallow solutions. Open APIs and customer focus drive innovation.
 By Akber Jaffer, Chief Commercial Officer for Marketplaces at Finastra.
By Akber Jaffer, Chief Commercial Officer for Marketplaces at Finastra.
One need only look to Amazon’s phenomenal evolution from book seller to orchestrator of global commerce to see the inherent value of multi-participant marketplaces, all built around customer needs. Across financial services, marketplaces are transforming industries historically fraught with inefficiencies, to the benefit of all participants and consumers of those services.
Marketplaces, or platforms as they are also known, can generally be categorized as vertical (focusing on a specific industry) or horizontal (relevant across multiple markets). Both vertical and horizontal can also be shallow (fulfilling a primary requirement) or deep (adding comprehensive services that tackle broader pan-industry challenges).
One of the simplest ways to illustrate this is by building on the work of the a16z team on shallow vs deep job platforms. A vertical, shallow marketplace would be one that serves a specific purpose and market, such as connecting participants (jobseekers and hiring companies) in a sector such as hospitality. A horizontal, shallow marketplace would use the same matching processes, technology and infrastructure to connect participants across multiple, or even all, industries.
But with the explosion of open APIs and a growing shift to build solutions in a more customer-centric way, so grows the appetite for deeper marketplaces. A vertical, deep marketplace would build on top of the core requirement (connecting job seekers with recruiters). a16z uses examples that include retraining bootcamps, career advisory services, right through to collaboration and even workforce management for post-employment support. New participants bring additional layers of value to tackle industry problems – which, in this case, could be the lack of jobs in hospitality during the pandemic – and open up opportunities to apply the model across multiple industries, to create a horizontal, deep marketplace.
It is this depth that drives a thriving ecosystem, across any marketplace. Even in a relatively finite vertical marketplace, the combination of open technology, the unbundling of services, and a customer-centric mindset is taking marketplaces from version 1.0; simply connecting or facilitating, to 2.0; orchestrating a launchpad for innovation and the creation of entirely new markets. Furthermore, new participants and new layers of value propagate marketplace adoption and interaction, whilst solving industry-wide challenges. These truly are virtuous circles that have the potential to transform every industry.
Deep Vertical Use Cases in Financial Services
1 – Residential Mortgage Marketplace
Deep vertical marketplaces continue to evolve having overcome, for many, a historic challenge of full digitization. Take the residential mortgage marketplace, not so long ago fraught with manual processes, time lags and inefficiencies for both lender and broker participants. Now, as we see in image 1, thanks to digitalization, automation and the prevalence of open APIs, the marketplace has been reconfigured around the participants’ and end customers’ journeys. Mortgage rates can be sourced and secured in real-time, and participants can benefit from extended services across the value chain; from market data to customer acquisition tools to collateral management.
It will not be long before new participants embed wider services – identity management, valuations, legal and conveyancing services, and so on, and widen still by bringing alternative lenders and real estate agents to the ecosystem for example.

Image 1 – Residential mortgage shallow and deep marketplaces
And this marketplace is an example of how a deep vertical can be flipped to become a deep horizontal solution, as image 2 shows, with many components able to transition to new markets and use cases.
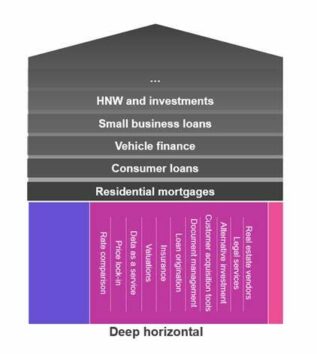
Image 2 – Residential mortgage deep vertical transition to deep horizontal
2 – Financial messaging marketplace
Likewise, financial messaging marketplaces have been reimagined to solve cross-industry inefficiencies and points of weakness. Across the value chain, areas such as payments, confirmations and settlements have been componentized, extended by the proliferation of value-add layers, such as fraud checking and blockchain distribution. Image 3 shows how simple the shift; taking a vertical, shallow marketplace to a multi-party industry marketplace that encourages new participants to join; firstly, to provide value to the ‘consumer’ – whether bank or corporate – and secondly, to access a functioning marketplace and reach new users at scale and speed.
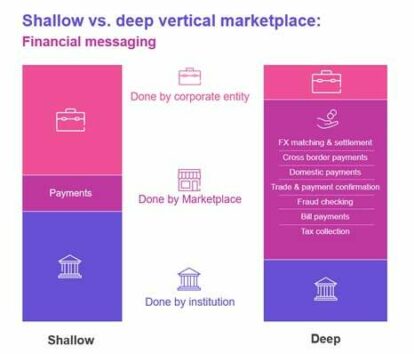
Image 3 – Financial messaging shallow and deep marketplaces
Banks, non-bank financial institutions and corporates can connect to traditional messaging, clearing and payment networks such as SWIFT – or newer bespoke payment channels such as Ripple or Mastercard Cross-Border Services – to exchange financial data and assets, and benefit from an extended ecosystem that can also identify fraudulent transactions for example. And it has the potential to embed new participants to generate new opportunities; geographical reach or through the addition of new payment rails for example, which in turn could serve new markets such as ecommerce participants that join. The entire value chain could expand to include Payment Service Providers (PSPs), challenger banks or other market participants, creating a wider distribution scope. Also, with the addition of value layers such as financial crime and blockchain components, the strength, transparency and security of the ecosystem could be significantly boosted.
3 – Trade Finance
My final example is that of trade financing (image 4). Globally, the gap – i.e. the difference between supply and demand of business funding in trade finance – has long been a tough issue to solve. Threatening to rise to $2.25tn by 2025 as a result of the pandemic, the problem is especially acute for SMEs, which employ half of the world’s working population and make up 90% of all enterprises globally.
The complexity of the problem lies in multiple contributory factors such as compliance constraints, labor intensive manual trade operations, a lack of visibility in credit quality, and a retrenchment of traditional lenders, and, here, a deep marketplace model could reduce these trade finance barriers through wider participation and digital capabilities.
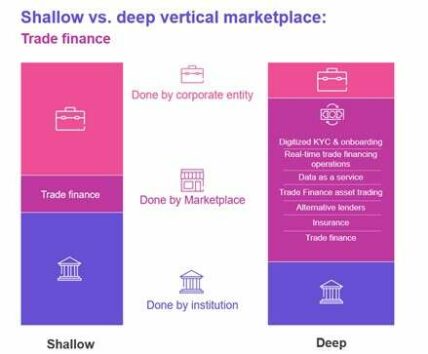
Image 4 – Trade finance shallow and deep marketplaces
As well as simplifying the KYC and onboarding elements, a marketplace can connect SMEs to both traditional and alternative financing, and furthermore enable trade finance asset trading, using enhanced risk modelling and data layers. Trade finance hubs and networks can connect in a single marketplace, fully validated, and paper gives way to fully digitized documentation for faster access to credit and more efficient distribution processes.
In this instance, not only does the marketplace orchestrate smoother financing flows through digitization but improve visibility into transaction risk – that generates more accurate data, that feeds risk engine models, that can be used to attract more funding…and so we begin to see another virtuous circle.
Deep marketplaces traits: Orchestrating all parties to connect, exchange, monetize and extend
The wider the remit of the marketplace, the more attractive it becomes to participants; adoption begets adoption and complex processes or market failures, such as access to trade finance or paper-based mortgage approvals are digitalized and enhanced, in a transparent and comprehensive way.
These deep marketplaces all share the same traits. Fundamentally, they orchestrate the participants and services for the benefit of entire industry sectors. They connect market participants, they facilitate an exchange – be it financial information, an asset or a service, they extend the value chain beyond the traditional transaction by being open and responsive to new innovations and markets, and every participant can monetize their part in the ecosystem on a usage basis, particularly if the marketplace can be flipped to a horizontal model to serve new markets. And through this orchestration, they solve historic, cross-industry problems.
Of course, just bringing participants to a marketplace is the first step. Like any form of embedded financial service, driving consumption is absolutely crucial. Across all of the marketplaces that we orchestrate at Finastra, active participation and volume are the prerequisites for a value-creating and sustainable model, so as much effort needs to be put into supporting participants as it does attracting them.
The article discusses the evolution of marketplace models in financial services, focusing on vertical and horizontal approaches.
Vertical marketplaces focus on specific industries, while horizontal marketplaces are relevant across multiple markets.
A deep marketplace adds comprehensive services to tackle broader industry challenges, beyond primary requirements.
Explore more articles in the Finance category
